Understanding 2-Ethyl-1-hexanethiol: An In-depth Perspective
Historical Development
Chemists first noticed the unique properties of 2-Ethyl-1-hexanethiol early in the twentieth century. Its distinct sulfur-containing structure stood out to researchers developing additives for lubricants and plasticizers. Over the decades, technology in petrochemicals brought new ways to synthesize and purify this compound, leading to its broader industrial use. Countries with advanced chemical industries, like Germany and the United States, invested heavily in manufacturing capacity for thiols, seeing potential for applications in everything from metal recovery to specialty polymers. As environmental laws evolved, production methods changed, focusing on higher purity and better containment of odors and emissions. The progress from basic lab synthesis to bulk-scale production mirrored the growth of the specialty chemicals sector itself.
Product Overview
2-Ethyl-1-hexanethiol, with the molecular formula C8H18S, falls into the family of aliphatic thiols. Its value comes from the unique combination of hydrophobic and reactive thiol characteristics. Demand emerged in markets like mining, oil refining, and plastics. Here, its combination of reactivity and relative compatibility with organic solvent systems created new processing advantages over bulkier or less reactive sulfidic additives. Suppliers focus on consistent quality, which remains critical, particularly in regions with stricter regulatory scrutiny or highly sensitive downstream applications.
Physical & Chemical Properties
A clear, colorless to pale yellow liquid describes most commercial batches. Its characteristic sulfurous odor, easily recognized even at low concentrations, makes ventilation essential during industrial handling. The thiol functional group gives this molecule a strong nucleophilic character, which opens routes for further chemical modification. Boiling points usually land near 186 °C, and the flash point sits at roughly 68 °C, putting it in a safe range for chemical plants designed for combustible liquids but still requiring basic fire mitigation. Lower water solubility keeps it out of aqueous environments, which can limit environmental dispersion, though its volatility keeps handling teams on their toes.
Technical Specifications & Labeling
Producers typically guarantee at least 98% purity, with low residual solvent and minimal side products. Labels carry hazard warnings tied to its flammability and acute toxicity, aligning with safety standards across the United States, EU, and Asian markets. All packaging includes batch numbers for traceability—a clear response to past problems with cross-contamination in the thiol market. The labeling reflects the industry shift toward robust product stewardship, born from both regulatory pressure and end-user demand for transparency.
Preparation Method
Often, chemists start with 2-ethylhexanol and hydrogen sulfide in the presence of an acid catalyst, driving a substitution reaction that efficiently swaps the alcohol group for a thiol. Each step must minimize byproduct formation. Producers rely on distillation and purification stages to meet product specifications. Precise temperature and pressure controls impact both yield and product safety, especially considering the toxic and malodorous nature of hydrogen sulfide. This chemistry draws on well-understood organic synthesis routes, but advanced process control sets apart superior suppliers.
Chemical Reactions & Modifications
2-Ethyl-1-hexanethiol reacts readily with metal ions, giving it a spot in the mining industry for separating valuable metals. Its thiol moiety allows participation in addition reactions with alkenes or alkynes, permitting custom molecule designs for polymers or surfactants. It also forms strong bonds with mercury and lead cations, helping decontaminate industrial effluents. Chemists take advantage of this reactivity for analytical standards and specialty reagents, synthesizing derivatives that fit exactly into complex organic frameworks.
Synonyms & Product Names
Other names appear in technical literature, including 2-Ethylhexane-1-thiol, Octyl mercaptan, EHSH, and even some local trade names linked to specific purity or stabilizer packages. Synonym recognition prevents confusion when ordering or discussing specifications between suppliers in different regions.
Safety & Operational Standards
With low evaporation thresholds and significant odor, this chemical gets handled in closed systems. Chemical plants invest in leak containment, vapor recovery, and rigorous employee training. Workplace exposure limits reflect both acute and chronic toxicity, tied in part to its thiol group, which can irritate eyes, respiratory tract, and skin. Personal protective equipment goes beyond gloves and goggles, often including full respirator suites for tank cleaning or spill response. Waste streams must be treated before disposal, following strict local regulations around thiols and hydrogen sulfide.
Application Area
Mining companies run flotation processes with 2-Ethyl-1-hexanethiol to selectively bind metals. In oil and gas, it reduces friction in refining flows and acts as a stabilizer for reactive agents. Plastic manufacturers use it to fine-tune polymerization reactions, securing chain-transfer reactions that optimize molecular weights in specialty plastics. Chemists see it as a reagent in laboratories experimenting with new organosulfur frameworks for pharmaceuticals and advanced materials.
Research & Development
R&D teams push for new preparation methods that limit byproduct odors and cut down waste. In specialty polymers, research evaluates thiol content as a way to give plastics new anti-corrosion properties. Academics also study its interactions with metal ions, drawing links to environmental decontamination. As more focus lands on sustainable chemistry, labs search for less energy-intensive synthesis methods and greener cross-coupling reactions, working to keep both yield and safety in line with mounting regulatory scrutiny worldwide.
Toxicity Research
Older studies raised red flags around both acute and long-term exposure, noting effects on the liver and kidneys in animal models and strong skin and respiratory irritation in workers. More recent surveys by global regulatory agencies—including the European Chemicals Agency—confirm these hazards, setting occupational exposure limits that push for improved ventilation and personal protection. Environmental groups watch for spills, given the compound's persistence and toxicity in aquatic organisms.
Future Prospects
Companies seek lower-odor thiols for greener production lines, while environmental controls around thiol emissions get tighter each year. Growing markets in Asia lead chemical plants to refine both purity and sustainability. Demand from electronics and renewable energy manufacturing keeps the compound relevant, as designers value tailor-made chemicals for specialty coatings and extraction agents. Digitalization in plant operations offers tools for safer, more efficient synthesis and tracking, helping keep production up to standard as regulations change. The future of 2-Ethyl-1-hexanethiol depends on balancing chemical performance with environmental and workplace safety, a challenge taken up each day in boardrooms, labs, and factory floors worldwide.
Getting to Know the Chemical
2-Ethyl-1-hexanethiol doesn’t show up in dinner table conversations, but it plays a quiet part behind many things people use every day. This compound, known for its strong sulfur scent, belongs to the class of organosulfur chemicals. Its unique structure gives it properties that industries have learned to rely on, especially in processes where selective chemical reactions or odor control matter.
Applications in Rubber and Plastic Manufacturing
Tire factories and rubber goods producers often turn to 2-Ethyl-1-hexanethiol as a modifier. Its ability to act as a chain transfer agent gives it a hand in steering polymer reactions. These reactions affect the strength and flexibility of the final products. A few decades working with manufacturing teams has shown the usefulness of this compound for getting rubber mixtures to behave just right under physical stress. Not every additive gives producers the fine control over material properties that this thiol offers.
A Role in Mining and Metal Extraction
Anyone who’s visited a mineral processing site has seen how complex ore extraction can get. 2-Ethyl-1-hexanethiol takes a central part as a flotation agent. Here, it helps separate valuable metals from their unwanted companions. The thiol binds preferentially with specific minerals, gathering copper, lead or precious metals. From my experience consulting at a copper mine in Northern Canada, operators count on this chemical to increase metal yields. Higher selectivity conserves resources, cuts costs, and reduces chemical waste, so the mines run cleaner.
Influence in Lubricants and Additives
Moving to industrial lubricants, 2-Ethyl-1-hexanethiol finds a place in specialized oils and greases. Its presence boosts the performance of extreme pressure additives, helping to prevent metal surfaces from welding under load. The gearboxes of freight elevators or turbines don’t fail often, thanks in part to such chemistry. Equipment reliability sky-rockets if the right thiol-based compounds are in play.
Controlling Odor and Protecting Surfaces
In the coatings world, 2-Ethyl-1-hexanethiol shows up in corrosion inhibitors and odor-masking agents. Its reactive sulfur group hooks onto metal surfaces, forming a protective barrier that holds rust at bay. At a refinery in Texas, environmental engineers taught me how small tweaks in inhibitor chemistry translate to years of added life for key plant equipment. On the odor side, strong scents from this thiol, properly managed, can mask unpleasant odors in certain industrial byproducts, making processing safer for workers.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Working with thiols means respecting their potential hazards. 2-Ethyl-1-hexanethiol demands careful handling—its vapors aren’t pleasant, and spills travel fast. Safety officers stress on proper PPE and ventilation. Many factories train their teams thoroughly, leaning on lessons learned from past accidents in chemical plants. Responsible companies also keep storage procedures up to date and monitor emissions.
Paths Toward Safer Use and Cleaner Production
Looking ahead, research continues into bio-based alternatives and greener production routes for thiols. Innovations often come from partnerships between industry and academia. Regulators encourage transparency, making it easier for buyers to choose safer products sourced under strict standards. The future will likely hold a tighter embrace of environmental stewardship in how chemicals like 2-Ethyl-1-hexanethiol are produced, transported, and put to use.
Understanding the Risks
2-Ethyl-1-hexanethiol sits on the shelf as a clear liquid, but it packs a punch if people skip the essential safety steps. In labs and plants where I’ve seen this chemical used, it puts eyes, skin, and lungs in the line of fire. Folks ignore the rotten-egg smell at their own risk—a strong, unpleasant scent means you know it's present, but never trust your nose alone.
Protecting Your Skin and Eyes
Protective gloves mean more than just any old pair you find lying around. Nitrile or laminated gloves act as a true barrier here. Splashes sting and leave folks with red, irritated skin for hours. In my experience, chemical-resistant goggles and a snug face shield save you from regret when unexpected splatter happens during mixing or pumping. A splash in the eye stings immediately and sends you scrambling to the eyewash station. Chemical burns around the eye area heal slow, so wrapping up exposed skin and eyes right from the start saves everyone a world of pain.
Breathing Easy
Even small spills send fumes through a room, fast. Vapor moves low to the ground and climbs quickly if there's no airflow. Plenty of times I've watched folks stop what they’re doing to crank up the extraction fan, but relying on open windows or basic fans does little. Local exhaust ventilation—hoods and systems pulling fumes directly away from you—makes a difference you can actually feel. Filtering masks rated for organic vapors step in when local ventilation can’t catch everything. Headaches and nausea signal folks have already breathed in too much, and long-term exposure puts the liver and nervous system at risk. Fresh air and solid ventilation keep everyone sharper on the job.
Storage and Spill Response
Leaky containers find their way into even the best-organized chemical rooms. 2-Ethyl-1-hexanethiol should never rest near food, oxidizers, or open flames. Flammable cabinets with solid mechanical locks and spill trays give peace of mind. I’ve seen rushed workers skip over double-checking seals, and one missed step ruins a long day. Spill kits built for thiols, not just generic solvents, handle these messes. Cat litter or sawdust won’t stop the smell or the chemical’s bite. Grab absorbent pads and neutralizers fit for sulfur compounds, then air out the place and dispose of waste using clear labels. It saves the next shift from running into an invisible hazard.
Training and Policy Matters
Talking through safety protocols isn’t enough. Real-world drills and demonstrations matter. I’ve had coworkers roll their eyes during chemical safety talks—until someone froze up during a small spill. Putting written policies into action means watching folks walk through donning PPE, handling fake leaks, and showing where kits and showers sit. Reviewing safety data sheets as a team brings the hazards home. Checking in with every new batch or container refresh keeps memory sharp and routine strong.
Health Monitoring
Even with sharp protocols, folks can develop sensitivity over time. Skin checks and throat irritation pop up first. Shortness of breath or headaches deserve fast attention. Providing access to occupational health professionals helps spot trouble long before it turns serious. Feedback loops with workers lead to better control steps. It shows respect for everyone’s well-being, not just compliance for compliance’s sake.
Smart Choices, Safer Work
Every time I see someone treat 2-Ethyl-1-hexanethiol like just another bottle, I remember stories about ruined days and avoidable injuries. Respect for this chemical isn’t about being scared; it’s about showing care for your crew and your own long-term health. Good gloves, fresh air, sharp minds, and open communication shape a workplace where everyone heads home safe.
Understanding the Formula of 2-Ethyl-1-hexanethiol
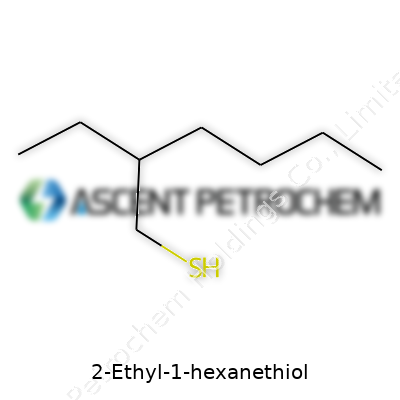
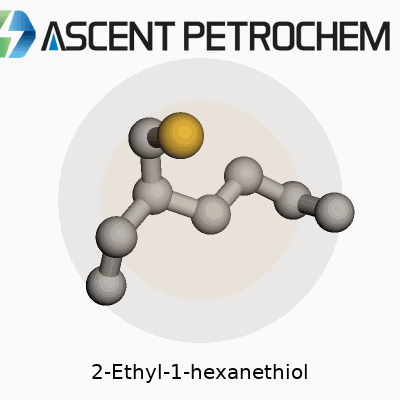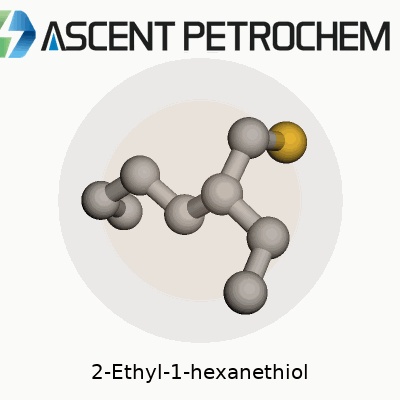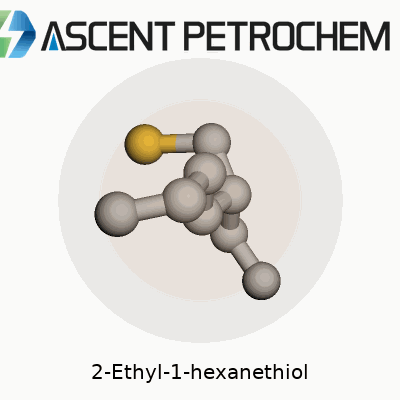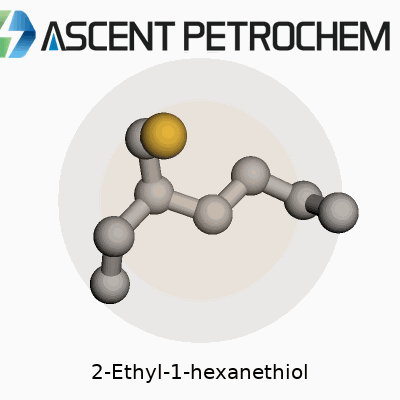
2-Ethyl-1-hexanethiol carries the molecular formula C8H18S. Laying it out piece by piece, you get a backbone made up of eight carbons, with a sulfur atom trading spots where most compounds would keep an oxygen or another carbon. Its full skeletal structure looks like this: CH3–CH2–CH2–CH(SH)–CH2–CH2–CH3, though that shorthand only hints at how this molecule actually folds and flexes in real life. Toss in the SH group at the end, and you’re dealing with a classic thiol, or mercaptan, known for their strong, sometimes pungent odor.
How Structure Impacts Behavior
That sulfur atom at the heart of 2-Ethyl-1-hexanethiol is not just a trivial swap. Working in labs and dealing with engineered materials, I’ve seen firsthand how that small change spins off big differences. Sulfur’s a bit of a wild card, less electronegative than oxygen, and much less polite about forming hydrogen bonds. So, what you end up with is a molecule that clings loosely to other compounds, giving it an edge where softness and flexibility matter in a final product. Its slightly branched carbon skeleton, triggered by the ethyl group on the second carbon, makes the molecule veer away from the flat, straight chains you find in plain old hexane.
Why Chemists Care: Use and Relevance
The structure of 2-Ethyl-1-hexanethiol lets it play a key part in crafting additives for lubricants and in certain polymers. The thiol group grabs onto metals and surfaces, which explains why industries line up for this compound when they want better adhesion or anti-corrosion properties. In the lab, I’ve seen this molecule act almost like a molecular glue, sticking where other additives fall short. Those SH groups are reactive, able to bind with metals and even tweak the surface chemistry of nanoparticles.
Imagine trying to coat a metal part with a protective layer that doesn’t flake off or break down under stress. Pulling a thiol like 2-Ethyl-1-hexanethiol off the shelf gives engineers new ways to build longer-lasting equipment. This results in less waste and fewer breakdowns—a win for efficiency and the environment. According to peer-reviewed journals, thiol-based corrosion inhibitors can extend metal service life by up to 30%, slashing maintenance costs significantly.
Potential Hazards and Responsible Use
With those benefits, though, you also bump into some ugly truths. Thiols are notorious for their sharp, unpleasant smell; even in tiny amounts, they’ll overpower a room. Given how easily the molecule sticks to skin and surfaces, handling demands care. Long sleeves, gloves, and good ventilation become as important as any molecule’s supposed utility. Chronic exposure to thiols can trigger headaches or nausea among sensitive workers, so process managers have to balance the functional gains with safe lab or plant conditions.
Room for Improvement
Chemists now look at ways to tame that odor without dulling the chemical’s edge. Advances in encapsulation technology or smart release coatings could help lock away the worst effects, freeing up the molecule for broader use. If regulatory guidance evolves to keep up with the science, teams can scale up applications without exposing workers or neighborhoods to these overwhelmingly strong smells. Keeping tabs on emerging safety studies, monitoring long-term impacts, and updating workplace controls make a real difference in shaping a more sustainable path for specialty chemicals like this one.
Why Care About Storage?
If you’ve spent time in a lab, you probably know the unmistakable stink of thiols. 2-Ethyl-1-hexanethiol ranks among the most pungent. But it’s not just about the fumes. Over the years, a few lessons have made it clear: a single leak or spill can mean problems for people, safety, and the bottom line. When I first started out, a mentor told me, “Respect your chemicals, or they’ll remind you who’s in charge.” I took that to heart, especially after tracking headaches and wasted days to poor storage.
Here’s what matters: this liquid is flammable, vapor-forming, and toxic if mishandled. Safety shouldn’t only be a checklist; it gives folks peace of mind and earns trust in any research or industrial space. Employees should never have to guess if a storage drum was closed right or left by a drafty window.
Where and How to Store
I always look for a cool, dry, well-ventilated room far from flames, sparks, or anything that can ignite vapors. If it smells strong, it needs better air flow. Dedicated flammable-chemical cabinets work best. Fire codes agree: keep this stuff away from sun, heat, and busy hallways. Don’t crowd incompatible materials — especially strong oxidizers — nearby.
Everyone talks about containers, but too often the wrong ones end up in the mix. Only use airtight glass or approved metal drums. Plastic sometimes softens or gets discolored after long storage, and a tiny crack can let those sharp odors spread. Always double-check the lids after each use.
Labeling and Access
I’ve seen disasters caused by sloppy or missing labels. Clear, bold, and waterproof tags cut down on confusion — no exceptions. If a transfer must happen, update the label then and there, not “later.” It saves time, money, and in some cases, calls to emergency responders. Limit access to trained workers and lock away the keys. The general public, and even untrained staff, have no business around these chemicals.
Checkups and Cleanliness
Leaks can creep up if routine inspections get skipped. A quick walk-through once a week is all it takes to spot trouble before it grows. Crusted caps, strange stains, and warped containers should trigger immediate cleanup and disposal. Training a couple of folks as internal safety watchdogs helps. Give them authority, and you’ll avoid “it’s not my problem” syndrome.
Disposal and Record-Keeping
Never pour chemicals like this down the drain or toss them in regular trash. Contact a licensed hazardous waste company and log every removal, no matter how small the amount. Well-kept records keep everyone honest and show regulators you take health and safety seriously.
Solutions and Vigilance
Some companies cut corners by skipping airflow checks or skimping on protective gear, but that always comes back to haunt them. Simple fixes like frequent checks, solid labels, and keeping incompatible chemicals apart add up. A tight protocol today avoids regulatory headaches and protects people down the road. Someone once told me: “Bad storage never stays a secret for long.” That stuck with me.
What Makes 2-Ethyl-1-hexanethiol Stand Out?
Anyone who has taken a chemistry class probably remembers the stench of thiols. 2-Ethyl-1-hexanethiol fits that notorious profile, packing a punch with a strong odor—hard to miss. This compound appears as a colorless to pale yellow liquid and doesn't want to dissolve in water. Yet, it flows pretty well with most organic solvents, like ether and alcohol. A long, flexible carbon chain with a sulfur-bearing thiol group gives it both its distinct character and smell. Take a whiff in a lab, and it leaves no room for doubt.
Physical and Chemical Personality
You will find its boiling point hovers around 189°C, which beats a lot of the lower-chain thiols that vaporize even sooner. The density cuts in at roughly 0.86 g/cm³ at room temperature, lighter than water, so spills float instead of diving to the bottom. Its refractive index of about 1.453 hints at its relatively complex structure compared to simpler alcohols or thiols. The vapor pressure is moderate, so it doesn't charge out of an open container as quickly as smaller, more volatile organics.
The chemical behavior comes down to the reactive thiol group—the -SH part. That bond snaps and reacts with metals, oxidants, and alkylating agents. Mixed with oxygen or strong oxidizers, it can really set off, forming disulfides. That outcome can be practical for anyone needing to link molecules together or make rubber more elastic. Just ask anyone working in rubber compounding; agents like 2-ethyl-1-hexanethiol modify polymer flexibility in a snap.
Human and Environmental Realities
Anyone handling this chemical remembers the safety protocol. Even slight skin exposure leaves a sticky, persistent smell. Inhalation leads to headaches or nausea if ventilation fails, so fume hoods stand as standard procedure.
On the industrial side, 2-ethyl-1-hexanethiol acts as a building block for specialty chemicals. Its thiol group latches onto metals, so it finds use in ore flotation. In fact, mining companies pay close attention to dosage, improving recovery of valuable ores such as copper and silver. Try to overdo it, and the product costs go through the roof, and downstream processing suffers.
Room for Improvement and Responsible Use
From a safety standpoint, more robust protection and sensors in workplaces make a difference. Proper ventilation needs ongoing investment. Chemical gloves and goggles come standard, but companies can drive down risks by switching to closed transfer systems that avoid open handling.
Waste disposal matters. Any leftover product, spills, and cleaning fluids deserve careful sequestration. Waterways pick up traces if care slips, harming aquatic life. Regular workers’ training and stricter spill containment rules keep risks in check. Local regulations demand careful alignment, so companies must keep up, not just with the latest process but with evolving environmental rules.
Bottom Line in Labs and Beyond
Working with 2-ethyl-1-hexanethiol reminds us that chemistry is hands-on and sometimes challenging. The compound’s character—volatile, smelly, but useful—underlines the constant trade-off in applied science: balancing utility, safety, and stewardship. Paying close attention to its unique properties not only prevents accidents but also leads to better outcomes for products and people alike. Each year, improvements in training, monitoring, and process design help reduce risks and unlock more diverse applications, so long as one keeps learning and adapting.
| Names | |
| Preferred IUPAC name | 2-Ethylhexane-1-thiol |
| Other names |
2-Ethylhexane-1-thiol
2-Ethylhexyl mercaptan Octyl mercaptan Ethylhexyl thiol 2-Ethyl-1-hexyl mercaptan |
| Pronunciation | /tuː ˈɛθɪl wʌn ˈhɛksænˌθaɪɒl/ |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | 15520-10-2 |
| Beilstein Reference | 1209267 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:84916 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL227782 |
| ChemSpider | 2025266 |
| DrugBank | DB14005 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 21a83847-f42a-49a4-9a95-5f34c71bdd3e |
| EC Number | 203-090-1 |
| Gmelin Reference | 104333 |
| KEGG | C19606 |
| MeSH | D000082206 |
| PubChem CID | 80588 |
| RTECS number | KI1575000 |
| UNII | 9M4I0VZ4F2 |
| UN number | UN3335 |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | DTXSID9054689 |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C8H18S |
| Molar mass | 162.32 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colorless to yellow liquid |
| Odor | unpleasant mercaptan-like |
| Density | 0.845 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| Solubility in water | Insoluble |
| log P | 3.51 |
| Vapor pressure | 0.35 mmHg (25°C) |
| Acidity (pKa) | 10.6 |
| Basicity (pKb) | 3.88 |
| Magnetic susceptibility (χ) | -74.5·10⁻⁶ cm³/mol |
| Refractive index (nD) | 1.4500 |
| Viscosity | 2.79 mPa·s (25 °C) |
| Dipole moment | 1.66 D |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Std molar entropy (S⦵298) | 247.6 J·mol⁻¹·K⁻¹ |
| Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH⦵298) | -222.2 kJ/mol |
| Std enthalpy of combustion (ΔcH⦵298) | -4885 kJ/mol |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling | GHS02, GHS06, GHS08 |
| Pictograms | GHS06,GHS08,GHS09 |
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H226, H302, H315, H319, H331, H335, H373, H411 |
| Precautionary statements | P210, P261, P273, P280, P305+P351+P338, P310, P501 |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | 1-3-0-W |
| Flash point | 74 °C (closed cup) |
| Autoignition temperature | 225 °C (437 °F; 498 K) |
| Explosive limits | 1.1% - 6.7% |
| Lethal dose or concentration | LD50 oral rat 1060 mg/kg |
| LD50 (median dose) | LD50 (median dose): 3450 mg/kg (rat, oral) |
| NIOSH | SN1925000 |
| PEL (Permissible) | PEL: 1 ppm (Skin) |
| REL (Recommended) | REL (Recommended Exposure Limit) for 2-Ethyl-1-hexanethiol: 1 ppm (5 mg/m³) |
| IDLH (Immediate danger) | 50 ppm |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds |
1-hexanethiol
2-ethylhexanol 2-ethylhexanal n-octyl mercaptan tert-octyl mercaptan |
